Django forms are a powerful feature of the Django Web Framework. It utilizes Python code to create and manipulate HTML forms. In this article, we look at how to implement a django form and customize it with Bootstrap 5 CSS framework.
When we create a form in django, by convention it is stored in forms.py inside your app's sub-directory.
|-- app/
|-- __init__.py
|-- forms.py
ModelForm and Form classes
In Django there are two major form classes used to create forms, the ModelForm class and Form class. The ModelForm attaches a Django model to the form were model attributes are used to create form fields. Having a Book model we can create a ModelForm from it.
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255)
author = models.CharField(max_length=255)
publish_year = models.IntegerField()
def __str__(self):
return self.title
We create a ModelForm class called BookModelForm based on our Book model.
from django import forms
from . models import Book
class BookModelForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Book
fields = ('title', 'author', 'publish_year',)
You only need to specify the model in the class meta and the fields inside a tuple or Python list.
The Form class allows you to create a form that is independent of any Django model.
from django import forms
class BookForm(forms.Form):
title = forms.CharField()
author = forms.CharField()
publish_year = forms.IntegerField()
The above code will create a Form class BookForm were each form field has to be expressly defined as a class attribute. Now we have the forms, import them into your views.
from django.shortcuts import render
from django import messages
from . forms import BookModelForm
class create_book_view(request):
# Initialize the model form with post data if any.
form = BookModelForm(request.POST or None)
if form.is_valid(): # Post data found and data is validated
form.save() # ModelForm saves using model attached to it.
messages.success(request, 'Book was created successfully')
return redirect('/')
# Pass the form object to the html file and return.
return render(request, 'create_book.html', {'form': form})
In our view function we initialize the form with the data from a post request, Because we are using a ModelForm we can call the form.save() method which will save the data in our database. Render the form in our HTML template with the code below.
The code example below assumes you are using bootstrap css framework.
{% extends 'layout.html' %}
<!-- Content --
{% block content %}
<div class="container">
<div class="col-md-6 offset-md-3">
<form method="post" action="">
{% csrf_token %} {{ form }}
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary"Save</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock content %}
Output
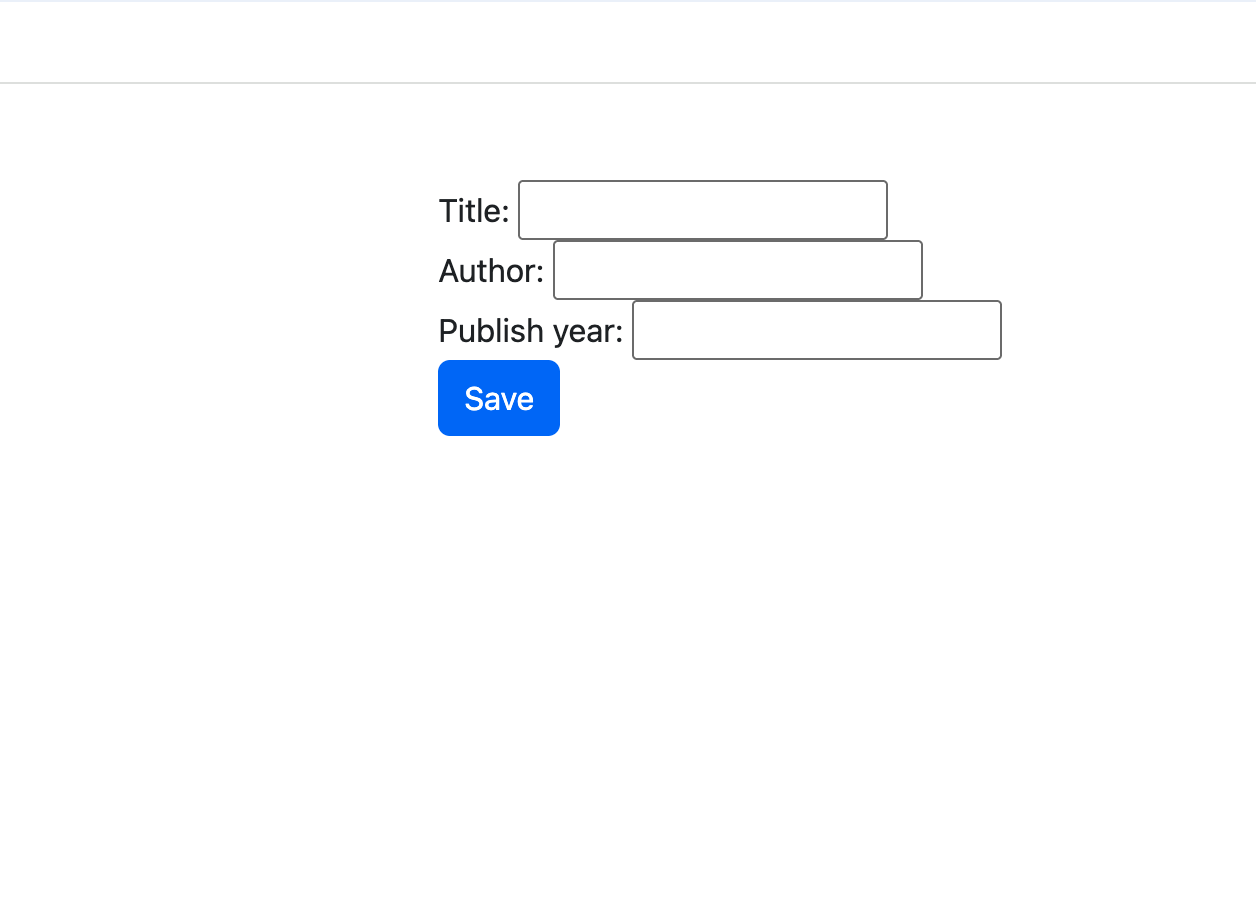
We have setup a basic django form, next, style it using Boostrap. In order for our forms to be styled properly we need to install django-crispy-forms. This is Python package that aids styling Django forms using different CSS framework.
Using Django Crispy Forms
Install django-crispy-forms with the command below.
pip install django-crispy-forms
Since we are using Bootstrap 5 we also need to install crispy-boostrap5 package.
pip install crispy-bootstrap5
Once they are both installed, inside of your project settings.py file add crispy_forms and crispy_bootstrap5 to INSTALLED_APPS.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'crispy_forms',
'crispy_boostrap5',
]
Finally, add the following settings configuration to your projects settings to tell django-crispy-forms to use Bootstrap 5 theme.
CRISPY_ALLOWED_TEMPLATE_PACKS = "bootstrap5"
CRISPY_TEMPLATE_PACK = 'bootstrap5'
In your HTML template, load crispy_forms_tags and apply the crispy template filter on the form.
{% extends 'layout.html' %} {% load crispy_forms_tags %}
<!-- Content --
{% block content %}
<div class="container">
<div class="col-md-6 offset-md-3">
<form method="post" action="">
{% csrf_token %} {{ form|crispy }}
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Save</button>
</form>
{% endblock content%}
</div>
</div>
Output
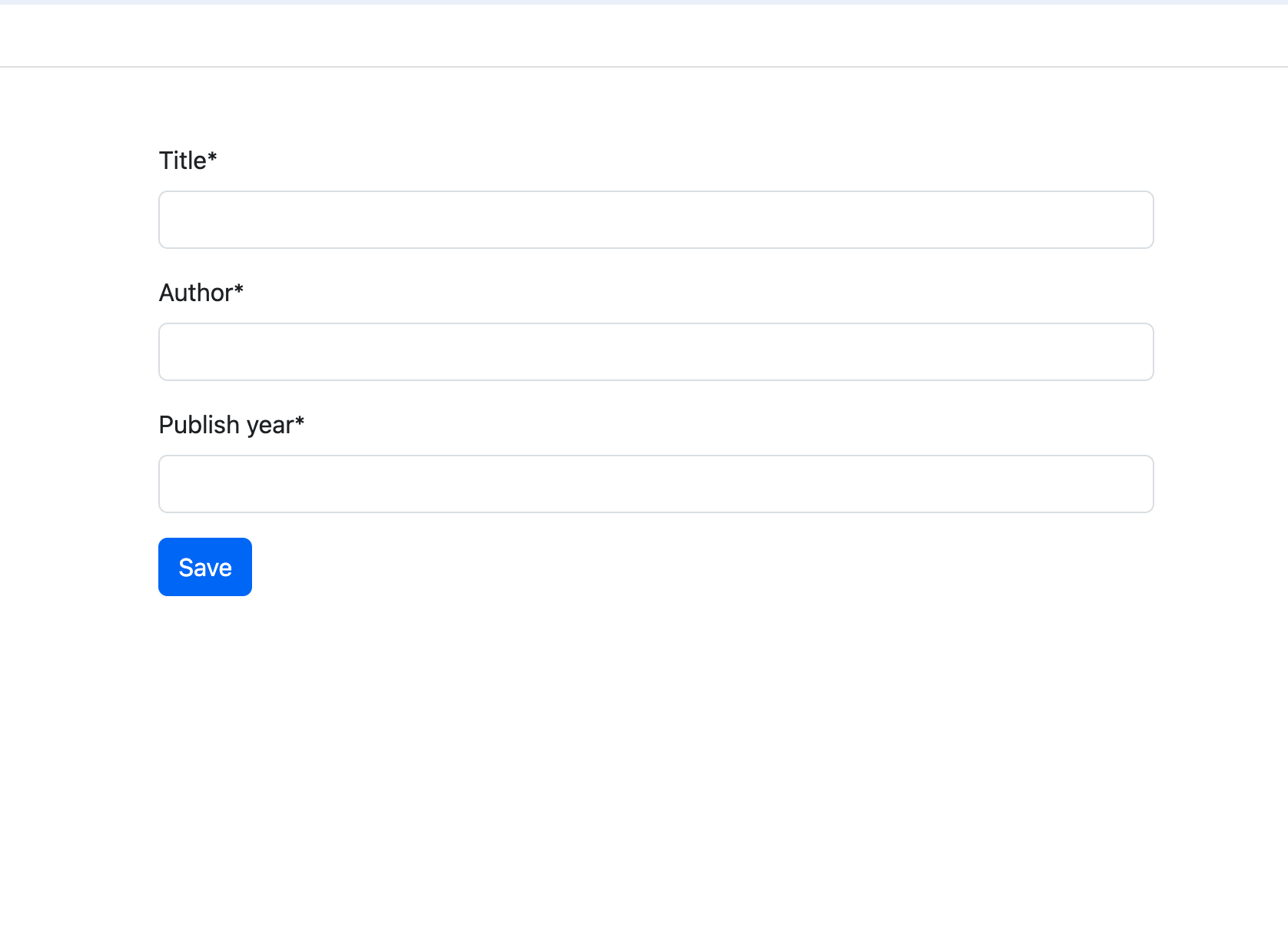
FormHelper
The FormHelper class is used for creating and customising forms in a pythonic way. Setup the FormHelper class in the model form's __init__ method. We also include some layout components so each field will be formated with the proper Boostrap classes.
from django import forms
from . models import Book
from crispy_forms.helper import FormHelper
from crispy_forms.layout import Layout, Row, Column, Submit
class BookModelForm(forms.ModelForm):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.helper = FormHelper()
self.helper.layout = Layout(
Row(
Column('title'),
Column('author'),
),
Column('publish_year'),
Submit('save', 'submit'),
),
class Meta:
model = Book
fields = ('title', 'author', 'publish_year',)
To render the form generated with the FormHelper class we use {% crispy form %} template tag instead of a template filter.
{% csrf_token %} {% crispy form %}
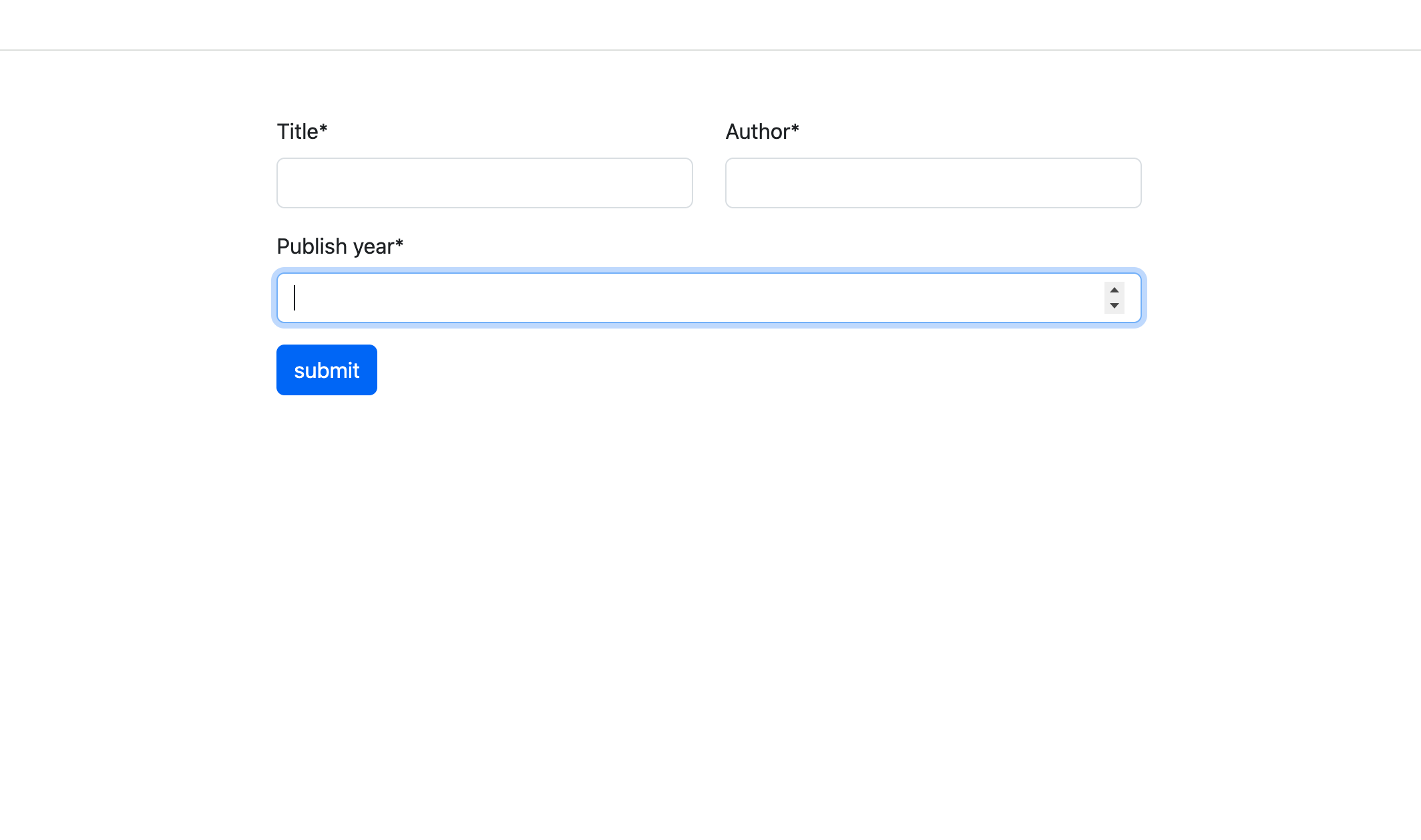
Django Crispy Forms + AJAX Request
Django crispy forms can also be integrated with AJAX requests. Setup an API using django-jsonview.
Install the Python package django-jsonview. This package is used to convert Django views into JSON API views.
pip install django-jsonview
Create a view function inside your views.py called create_book_api. This view will handle the any POST request sent via Javascript.
from crispy_forms.utils import render_crispy_form
from jsonview.decorators import json_view
from . forms import BookModelForm
@json_view
def create_book_api(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
form = BookModelForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return {'success': True}, 201 # 201 is HTTP code for created
rendered_form = render_crispy_form(form, helper=form.helper)
return {'succcess': False, 'form': rendered_form}, 400 # 400 is HTTP code for bad request
return {'success': False}, 405 # 405 us HTTP code for method not allowed
If the form is valid we return a json response with status 201. If the form is invalid, an error feedback HTML form is generated at the backend with render_crispy_form function and returned as json response.
The create_book_api is used to update the form on the browser after it has been rendered.

